防抖节流
2024年2月7日大约 5 分钟
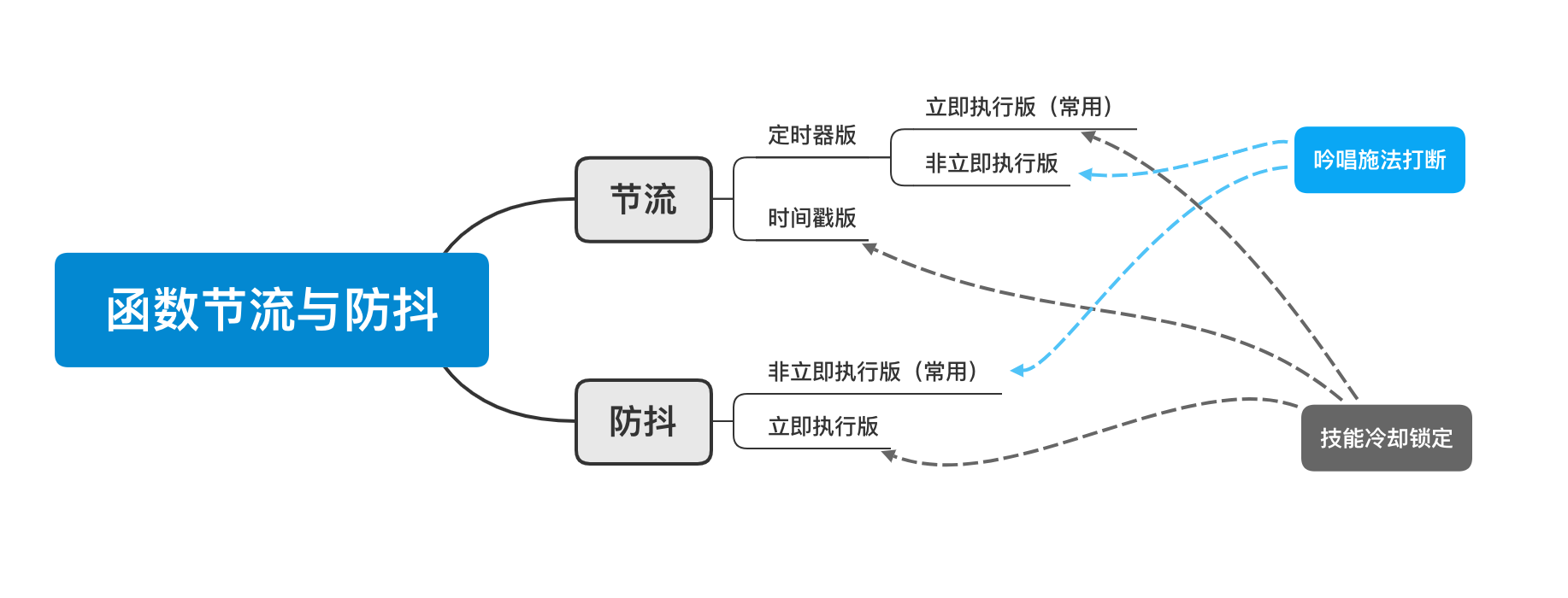
在事件触发频繁如 resize、scroll、mousemove 等场景中,为了减少处理开销,采用节流或防抖限制函数的执行次数。共同点都是在规定时间段内频繁触发事件只执行一次函数。
节流:功能函数 fn 在定时器外 或 没有定时器,则在固定时间段开始时立即执行,即立即执行版。类比技能冷却时间,释放技能后进入冷却。连续触发事件但是在 n 秒中只执行一次函数。节流会稀释函数的执行频率。
防抖:功能函数 fn 在定时器内,则在固定时间段结束时执行,即非立即执行版。类比吟唱施法时间,打断则重来。触发事件后 n 秒后才执行函数,如果在 n 秒内又触发了事件,则会重新计算函数执行时间。
节流(throttle)
立即执行版(常用)
功能函数在定时器外:触发事件后立即执行函数再进入规定冷却时间
function throttle(fn, delay = 500) {
let timer = null
return function() {
if (!timer) {
fn.apply(this, arguments) // 注意在定时器外(冷却)
timer = setTimeout(() => {
timer = null
}, delay)
}
}
}
window.onscroll = throttle(() => console.log('scroll'), 1000) // 业务代码
思路:
- 每当触发事件调用节流函数,如果当前没有计时器,就执行功能函数
fn,并创建一个计时器,计时器计时完毕后清除自己。 - 在规定时间内不断调用节流函数,由于定时器已经存在,不执行功能函数
fn。
非立即执行版
功能函数在定时器外:非立即执行就不是节流了。
function fakeThrottle(fn, delay = 500) {
let timer = null
return function() {
if (!timer) {
timer = setTimeout(() => {
timer = null
fn.apply(this, arguments) // 注意在定时器内(吟唱)
}, delay)
}
}
}
window.onscroll = fakeThrottle(() => console.log('scroll'), 1000) // 业务代码
时间戳版
// 方案一
function throttle(fn, delay = 500) {
let previous = 0
return function() {
let now = Date.now()
if (now - previous > delay) {
fn.apply(this, arguments)
previous = now
}
}
}
window.onscroll = throttle(() => console.log('scroll'), 1000) // 业务代码
// 方案二(coderwhy)
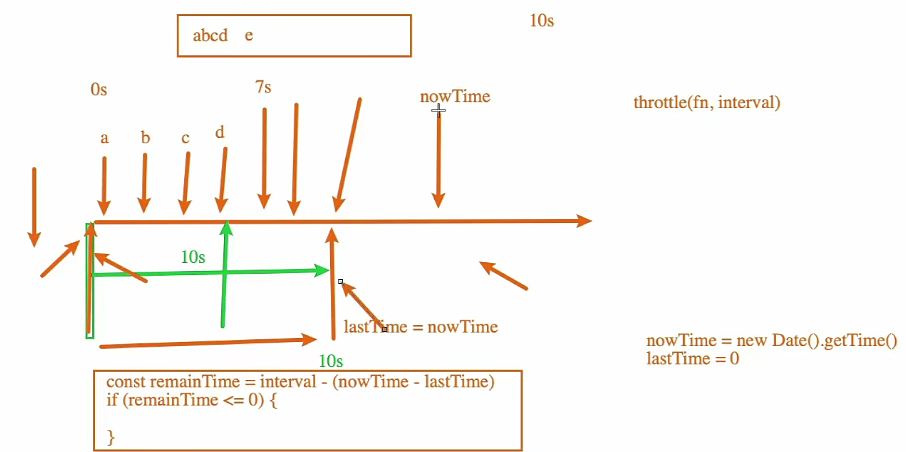
function throttle(fn, interval, options) {
// 1.记录上一次的开始时间
let lastTime = 0
// 2.事件触发时, 真正执行的函数
const _throttle = function() {
// 2.1.获取当前事件触发时的时间(输入第一次会触发,因为Date().getTime()一开始是一个非常大的数)
const nowTime = new Date().getTime()
// 2.2.使用当前触发的时间和之前的时间间隔以及上一次开始的时间, 计算出还剩余多长事件需要去触发函数
const remainTime = interval - (nowTime - lastTime)
if (remainTime <= 0) {
// 2.3.真正触发函数
fn()
// 2.4.保留上次触发的时间
lastTime = nowTime
}
}
return _throttle
}
应用场景:
- 监听页面滚动事件。
- 鼠标移动事件。
- 频繁点击按钮事件。
- 飞机大战游戏子弹射击。
- 生活例子:1 分钟后没有问题就下课 →10s 张三 → 重新等 1 分钟 →30s 李四 → 再重新等 1 分钟。
防抖(debounce)
非立即执行版(常用)
功能函数在定时器外:触发事件后吟唱规定时间后再执行函数。
function debounce(fn, delay = 500) {
// 1.定义一个定时器,保存上一次的定时器
let timer = null
// 2.真正执行的函数
return function(...args) {
if (timer) {
// 把上一次的timer定时器取消掉
clearTimeout(timer)
}
// 延迟执行
timer = setTimeout(() => {
// 外部传入的真正要执行的函数
// 这里的this是input标签本身,不用apply绑定就指向window
fn.apply(this, args)
}, delay)
}
}
let input = document.querySelector('input')
input.oninput = debounce(() => {
console.log(input.value) // 业务代码
}, 1000)
立即执行版
加入immediate和isInvoke变量来实现。
// 输入第一次就要立即发送请求
function debounce(fn, delay, immediate = false) {
// 1.定义一个定时器, 保存上一次的定时器
let timer = null
let isInvoke = false
// 2.真正执行的函数
const _debounce = function(...args) {
// 取消上一次的定时器
if (timer) clearTimeout(timer)
// 判断是否需要立即执行
if (immediate && !isInvoke) {
fn.apply(this, args)
isInvoke = true
// immediate=false 理论上可以,但是不好。
} else {
// 延迟执行
timer = setTimeout(() => {
// 外部传入的真正要执行的函数
fn.apply(this, args)
isInvoke = false
// immediate=true 理论上可以,但是不好。
}, delay)
}
}
return _debounce
}
思路:
- 每当触发事件调用防抖函数,就创建一个计时器,如果新创建计时器前存在一个计时器,就清除旧的计时器,保留新创建的计时器。
- 在规定时间内不断调用防抖函数,会不断创建新的计时器替代旧的计时器。某一计时器坚持规定时间不被替代,才执行功能函数。
通俗理解:像是擂台赛一样,谁在擂台上坚持一段时间,无人挑战,就是最终的胜出者。或像是拍卖一样,谁出价坚持一段时间,无人再次出价,就是最终的竞得者。
// 节流就是「技能冷却中」
const throttle = (fn, delay = 500) => {
let timer = null
return (...args) => {
if (timer) {
return
}
fn.call(undefined, ...args)
timer = setTimeout(() => {
timer = null
}, delay)
}
}
window.onscroll = throttle(() => console.log('hi'), 1000) // 业务代码
// 防抖就是「回城被打断」
const debounce = (fn, delay = 500) => {
let timer = null
return (...args) => {
if (timer !== null) {
clearTimeout(timer)
}
timer = setTimeout(() => {
fn.call(undefined, ...args)
timer = null
}, delay)
}
}
let input = document.querySelector('input')
input.oninput = debounce(() => {
console.log(input.value) // 业务代码
}, 1000)
应用场景:
- 搜索输入框内输入关键字进行联想(如在 1s 内输入 coderwhy,总共只发送一次请求进行联想,每个字符进行 500ms 联想,每次输入一个字符重新等待 500ms)。
- 监听浏览器滚动事件。
- 生活例子:10 点下课,1 分钟内只回答一个同学的问题。
第三方库
- lodash:underscore 升级版,更笨重,很久没更新了。
- 引入 CDN,
xxx.oninput=_.throttle(inputChange,2000)。
- 引入 CDN,
- underscore:更轻量,仍在维护。
- 引入 CDN,
xxx.oninput=_.debounce(inputChange,2000)。
- 引入 CDN,
Loading...